A Technical Deep Dive into the Sony IMX462 Starvis Sensor: The Leader in Ultra Low-Light Performance
In the realm of industrial and embedded vision, the ability to capture high-quality images in challenging lighting conditions is a critical requirement. While many sensors claim low-light capabilities, few can match the performance of the Sony IMX462, a flagship model in the Starvis family. This article provides a comprehensive technical analysis of the IMX462’s specifications, core advantages, current market demand, and key application scenarios for industrial and commercial use.
Technical Specifications and Core Performance Metrics
The IMX462 is a 1/2.8-inch CMOS image sensor with an effective pixel count of 1920 (H) × 1080 (V), delivering a crisp Full HD (2.9 MP) resolution. Its defining feature, however, is not its pixel count but its exceptional sensitivity. The sensor boasts a large 2.9µm pixel size, a key factor in its superior performance.
Key Parameters:
- Sensor Type: Back-Illuminated (BSI) CMOS
- Optical Format: 1/2.8-inch
- Pixel Size: 2.9µm
- Resolution: 1920(H) x 1080(V) (Full HD)
- Maximum Frame Rate: Up to 60fps
- Sensitivity: This is where the IMX462 truly shines. It achieves a remarkable sensitivity of 2580 mV (typ.) at 1 lux, and its NIR sensitivity is particularly noteworthy.
- Dynamic Range: The sensor features a high dynamic range (HDR) mode, crucial for scenes with extreme variations in light and shadow.
The Back-Illuminated (BSI) structure is fundamental to its high sensitivity. Unlike front-illuminated sensors where wiring can obstruct light paths, BSI sensors position the photodetector closer to the lens, capturing more photons and significantly improving quantum efficiency, especially in the near-infrared (NIR) spectrum.
The Core Advantage: Unrivaled Near-Infrared (NIR) Performance
The IMX462’s preeminence stems from its advanced NIR performance. The sensor’s large pixel size, combined with Sony’s proprietary Starvis technology, enables it to capture a vast amount of light, particularly in the NIR region (700-1000nm), where typical CMOS sensors struggle. This allows for clear, detailed monochrome imaging in complete darkness using IR illuminators, and high-quality color imaging in extremely low-light conditions with minimal ambient light.
IMX462 vs. Other Brands: A Comparative Analysis
When a technical engineer or product manager evaluates a sensor for ultra low-light applications, the comparison often extends beyond basic specifications.
- IMX462 vs. Omnivision/Onsemi Sensors: While competitors offer similar resolutions, the IMX462's Starvis architecture provides a demonstrably lower noise floor and higher signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in low-light environments. This results in cleaner, more usable images, reducing the need for extensive post-processing and improving the accuracy of subsequent AI/ML algorithms. The superior NIR sensitivity also gives it a significant edge for applications requiring covert IR illumination.
- IMX462 vs. Standard CMOS Sensors: The difference is night and day. Standard sensors often produce grainy, underexposed images in low-light, making them unsuitable for critical applications. The IMX462, on the other hand, can still deliver a recognizable and detailed image, effectively extending the operational window of a vision system from daytime only to a 24/7 capability.
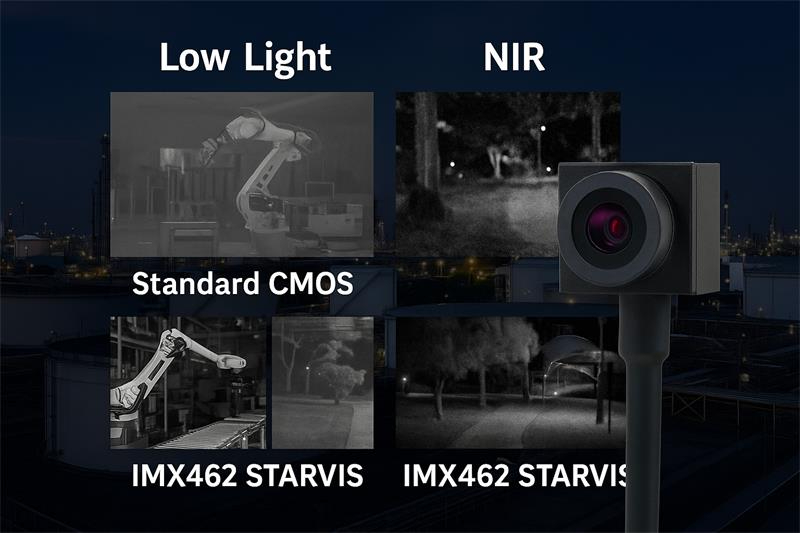
Current Market Demand and Driving Factors
The demand for the IMX462 is currently robust and shows a clear upward trend, driven by industries with unique low-light requirements.
- Cost-Performance Balance: As a 2.9MP sensor, it offers a more cost-effective solution than its 4K counterparts like the IMX415, while delivering a level of low-light performance that is unmatched in its class. This makes it an ideal choice for projects where budget is a consideration but performance cannot be compromised.
- Supply Chain Stability: As a mainstream Sony sensor, the supply chain for the IMX462 is mature and stable, which is a critical factor for OEM clients and manufacturers planning for mass production.
Primary Industrial and Commercial Applications
The IMX462’s unique technical profile makes it the sensor of choice for specialized applications that operate in challenging conditions.
- Robotics and Autonomous Systems: For Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) and other robotic systems operating in warehouses, hospitals, or outdoor environments, the IMX462 provides reliable vision for navigation, object detection, and situational awareness in dimly lit corridors or during late shifts.
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): The sensor is widely used in drones for night-time security, search and rescue, and industrial inspection (e.g., inspecting power lines or pipelines). Its ability to see in near-total darkness, when paired with an IR illuminator, is a game-changer for these missions.
- High-End Security and Surveillance: In professional security cameras, the IMX462 enables crystal-clear monitoring of perimeters, streets, and parking lots during the night, capturing critical details that would be lost with a standard sensor.
- Scientific Research and Life Sciences: From capturing animal behavior in the wild to low-light microscopy, the IMX462 provides the sensitivity required for high-quality data acquisition in light-starved environments.

In conclusion, the Sony IMX462 is not just another CMOS sensor; it is a specialized tool for developers and engineers building vision systems for the most demanding low-light applications. Its superior NIR sensitivity, low noise performance, and a strong market presence make it a top contender for any project where the ability to "see in the dark" is a non-negotiable requirement.
Relative Articles and Starvis IMX462 usb camera module links
1, Extreme Low-Light 0.001Lux IMX462 STARVIS USB Camera Module
2, IMX462 vs IMX307: Low-Light Starvis Sensor Comparison
3, STARVIS IMX415 vs IMX462 how to choose for your projects
4, Extreme Low-Light 0.001Lux IMX462 STARVIS USB Camera Module ( NOVEL PRODUCTS)
5, SONY STARVIS SENSOR AND CAMRAS FROM NOVEL MANUFACTURE LIMITED


