
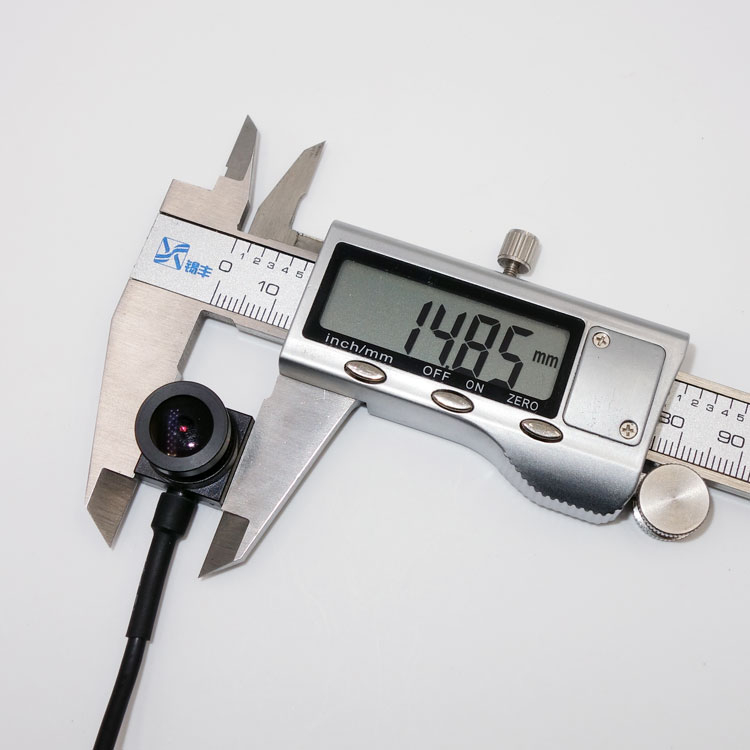
Embedded vision systems are specialized computing platforms that integrate image capture, processing, and analysis directly into a device or machine. Unlike traditional PC-based setups, these systems combine compact cameras, processors, and software into a self-contained unit that can perform real-time visual tasks.
At their core, embedded vision solutions enable machines to see, interpret, and act. They can identify defects on a production line, guide autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), verify assembly accuracy, or monitor industrial facilities in low-light environments. The miniaturization of high-performance image sensors, especially Sony’s STARVIS family, has accelerated the adoption of embedded vision in diverse industries.
Embedded systems are everywhere in modern industry and daily life. Below are typical examples where vision technology is embedded:

Although often used interchangeably, embedded vision and machine vision differ in scope and implementation:
In other words, machine vision = centralized power, while embedded vision = distributed intelligence. Both approaches are valuable, but the shift toward Industry 4.0 has made embedded vision the go-to choice for applications demanding small size, portability, and real-time adaptability.
Embedded systems can be categorized into four main types, each with distinct characteristics:
In Houston, Texas, an oil and gas refinery integrated STARVIS-based USB cameras into its pipeline inspection robots. The refinery previously relied on manual checks, which were time-consuming and prone to errors in poorly lit areas. By adopting low-light embedded vision modules, inspectors could remotely monitor valve conditions and detect gas leaks in real time. This improved both safety compliance and inspection efficiency, while reducing downtime.
At the Port of Miami, embedded vision modules were installed on container-handling cranes to support automated stacking and alignment. Using compact USB cameras with HDR capability, cranes can identify container codes even under direct sunlight or shadowed conditions. This increased throughput by nearly 20% while reducing human error. Embedded vision not only accelerated logistics but also made operations safer for ground personnel.
In Stuttgart, Germany, a leading automotive OEM deployed embedded cameras for weld seam inspection. Using real-time vision modules with high dynamic range, the system identified micro-defects during production without halting the line. Unlike traditional machine vision setups that required large PCs, these embedded solutions were installed directly on robotic arms, cutting down integration complexity and floor space usage. The result was a 15% increase in defect detection rates and lower rework costs.
At Shenzhen Novel Electronics Limited, we specialize in delivering ultra-compact, high-performance embedded vision solutions for robotics, industrial equipment, drones, and IoT devices. Our flagship products include:
By combining miniaturization, autofocus technology, and wide-angle imaging, our solutions empower robotics and industrial systems to achieve clearer vision, faster integration, and higher efficiency.

Embedded vision systems are at the heart of industrial transformation in the US and Europe. From oil refineries in Texas to port logistics in Florida, and automotive assembly lines in Germany, compact and efficient vision modules are proving their value in mission-critical environments.
With our 15×15 mm micro USB cameras and 6×6 mm wide-angle AHD modules, Novel Electronics provides the ideal building blocks for next-generation embedded vision — delivering clarity, precision, and adaptability to meet the growing demands of Industry 4.0.